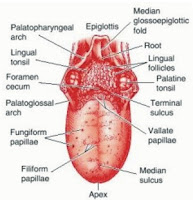
The tongue is a powerful muscle involved in the critical functions of speaking, chewing and swallowing. Taste buds cover the upper surface of the tongue. A variety of diseases and disorders can affect the tongue including infections, injuries, chronic irritation, abnormal tissue growth and congenital conditions. Many tongue disorders are short-lived; others may cause long-term difficulties, requiring ongoing medical management.
Leukoplakia
Leukoplakia is a painless grey or white patch on the tongue that develops in response to chronic irritation. These patches can also develop on the inner cheek regions of the mouth. Cigarette or pipe smoking and use of chewing tobacco increase the risk for development of leukoplakia. Irritation caused by poorly fitting dentures or rough spots on the teeth can also lead to leukoplakia. The University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center reports that approximately one-quarter of leukoplakia patches are cancerous or precancerous. A variant of this disorder known as hairy leukoplakia is caused by the Epstein-Barr virus, and mostly commonly occurs in people with a weakened immune system
Leukoplakia
Leukoplakia is a painless grey or white patch on the tongue that develops in response to chronic irritation. These patches can also develop on the inner cheek regions of the mouth. Cigarette or pipe smoking and use of chewing tobacco increase the risk for development of leukoplakia. Irritation caused by poorly fitting dentures or rough spots on the teeth can also lead to leukoplakia. The University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center reports that approximately one-quarter of leukoplakia patches are cancerous or precancerous. A variant of this disorder known as hairy leukoplakia is caused by the Epstein-Barr virus, and mostly commonly occurs in people with a weakened immune system